Testing with Node.js and io.js
- Quick start
- Line endings
- Selecting Node.js or io.js version
- Testing under multiple versions of Node.js or io.js
- Deploying a Node.js website to Azure
- Authenticating NPM for publishing packages
- Known issues
Quick start
Put this simple appveyor.yml to the root of your repository and it should work for the most Node.js projects out there:
# Test against the latest version of this Node.js version
environment:
nodejs_version: "6"
# Install scripts. (runs after repo cloning)
install:
# Get the latest stable version of Node.js or io.js
- ps: Install-Product node $env:nodejs_version
# install modules
- npm install
# Post-install test scripts.
test_script:
# Output useful info for debugging.
- node --version
- npm --version
# run tests
- npm test
# Don't actually build.
build: off
Line endings
By default, Git on build workers is configured with git config --global core.autocrlf input which means your repo is cloned “as is” without fixing new lines on Windows. If you have a file with a string abc\n line2 it will be checked out exactly as abc\n line2 and if there is line1 \r\n line2 in the repo you’ll get the same on checkout. See this SO answer explaining in details core.autocrlf modes.
However, if you expect Git to fix line endings on Windows and checkout all strings with \r\n you could tell Git doing that during init phase of your build which occurs before cloning command:
init:
- git config --global core.autocrlf true
We do not recommend relying on core.autocrlf value set on AppVeyor build workers and always explicitly change this setting during the build or have it configured per-repository.
Selecting Node.js or io.js version
Build workers have the most recent versions of Node.js and io.js pre-installed - both x86 and x64. If you do nothing your scripts will run under Node.js 4.7.x (x86) (at the time of writing).
To switch to a different version of Node.js or io.js use the following PowerShell command:
Install-Product node <version> [x86|x64]
<version> can be specified as MAJOR to install absolute latest version of Node.js or io.js, MAJOR.MINOR to install the latest Node.js or io.js build or MAJOR.MINOR.BUILD to install specific build. When MAJOR part of the <version> is 1 then io.js is installed.
For example to switch runtime to the latest version of Node.js use this command (at the time of writing this is the latest 7.x branch):
Install-Product node ''
To switch Node.js to the latest available 6.x branch use:
Install-Product node 6
To select specific x64 version of Node 6.9.3:
Install-Product node 6.9.3 x64
Any 1.x version automatically assumes you want io.js, so to switch to the latest version of io.js use this command:
Install-Product node 1
In appveyor.yml you should prefix command with ps to tell AppVeyor it’s PowerShell:
install:
- ps: Install-Product node 1
How that works
Pre-installed Node.js distributives are stored in C:\avvm\node folder. When you run Install-Product node command it’s, basically, moving nodejs or iojs folder from there to Program Files, so the switch is very quick. To check what versions are available on build worker you could do dir C:\avvm\node.
The following paths are always added to PATH environment variable:
C:\Program Files (x86)\nodejs
C:\Program Files (x86)\iojs
C:\Program Files\nodejs
C:\Program Files\iojs
C:\Users\appveyor\AppData\Roaming\npm
Installing any version of Node.js or io.js
Sometimes pre-installed versions of Node.js or io.js are little behind (this is especially true for io.js), but what if you need to test under bleeding edge. You could use another PowerShell cmdlet which does full re-install of Node.js or io.js to a selected version.
Update-NodeJsInstallation <version> [x86|x64]
Here <version> is exact version of Node.js or io.js.
For example the following command will download and install Node.js 5.12.0:
Update-NodeJsInstallation 5.12.0
There is a helper cmdlet checking remote dist directory of Node.js or io.js to determine absolute latest build available:
Get-NodeJsLatestBuild <major>.<minor>
It could be used together with previous cmdlet to always install the latest build, for example:
Update-NodeJsInstallation (Get-NodeJsLatestBuild 1.0)
Testing under multiple versions of Node.js or io.js
AppVeyor enables easy testing against multiple combinations of platforms, configurations and environments with build matrix.
To test under latest version of Node.js and io.js you can specify in appveyor.yml:
environment:
matrix:
# node.js
- nodejs_version: "4"
- nodejs_version: "6"
# io.js
- nodejs_version: "1.0"
install:
- ps: Install-Product node $env:nodejs_version
To allow failing jobs for bleeding-edge Node.js versions:
matrix:
allow_failures:
- nodejs_version: "7"
What if you need to test under specific version of Node.js for both x86 and x64 platforms? You could add another “dimension” to the matrix, for example:
environment:
matrix:
- nodejs_version: "4"
- nodejs_version: "6"
platform:
- x86
- x64
install:
- ps: Install-Product node $env:nodejs_version $env:platform
This configuration will produce a build with 4 jobs for all combinations of node version and platform:
Node.js 4.x x86
Node.js 4.x x64
Node.js 6.x x86
Node.js 6.x x64
Deploying a Node.js website to Azure
You can use Web Deploy to deploy your Node.js website to Azure.
Authenticating NPM for publishing packages
For publishing packages to NPM registry during the build npm client should be authenticated. On your development machine you run npm adduser command to set npm credentials.
On AppVeyor build worker you don’t need to run npm adduser, but you can just move npm authToken from your local machine to a build VM. This is what you have to do:
- Do
npm adduseron your local dev machine. - Copy
authTokenvalue from%userprofile%\.npmrcon your local machine. - In AppVeyor, on Environment tab of project settings add a new environment variable with name
npm_auth_tokenand the valued copied on step 2. Click “lock” icon to mark the variable as “secure” (so it won’t be available for PR builds). - Add to your
appveyor.yml:
install:
- ps: '"//registry.npmjs.org/:_authToken=$env:npm_auth_token`n" | out-file "$env:userprofile\.npmrc" -Encoding ASCII'
- npm whoami
npm whoami should display your username.
Known issues
Wrong output encoding
When running npm install (or any other Node.js program writing to a console) you may notice that Unicode symbols written to build console look wrong:
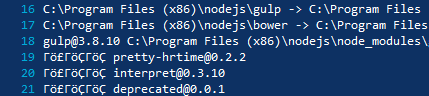
This is because you are calling that program from PowerShell:
- ps: npm install
To fix that run it in “shell” mode:
- npm install
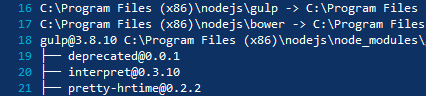
At the moment it seems to be an issue with PowerShell and the way it redirects output from console apps to a custom PowerShell host.
Garbled or missing output
Sometimes you may notice that output of some Node.js programs (especially those ones actively writing to both StdOut and StdErr) is garbled or missing.
In two words, there was Windows-specific issue in Node.js with non-blocking StdErr (joyent/node#3584) which was fixed in this pull request joyent/node#7196 and finally landed in Node.js v0.11.12 (joyent/node@20176a9). There is a great discussion of this problem.
Solution - run your tests under the latest Node.js.
Locking errors (EPERM, EEXIST, tgz.lock)
Sometimes you may encounter sporadic “lock” errors that might look like:
npm ERR! Error: EPERM, open 'C:\Users\appveyor\AppData\Roaming\npm-cache{something}-package-tgz.lock'
npm ERR! EEXIST, open '{some-path}\npm-cache{something}-package-tgz.lock'
By default, Node.js comes with pre-installed npm of version 1.x. However, most of these “racing condition” issues were fixed in npm 2.0.
Solution - install npm 2.0:
npm -g install npm@2
set PATH=%APPDATA%\npm;%PATH%
More info about npm troubleshooting on Windows.