Deploying to remote servers with AppVeyor Deployment Agent
AppVeyor Deployment Agent (Deployment Agent) is a service running on remote server and helping to deploy select artifact as IIS website or Windows application/service.
- Software requirements
- Installing AppVeyor Deployment Agent
- Unattended Deployment Agent installation
- What artifacts can be deployed
- How to get named artifacts
- Configuring deployment settings
- Global settings
- Overriding settings while deploying from build
- Deploying artifact package as IIS web site
- Deploying artifact package as a Windows application
- Deploying artifact package as a Windows service
- Publishing SSDT package artifact to SQL Server
- Installing MSI package artifact on remote machine
- Running PowerShell scripts on target server during deployment
- Troubleshooting
Software requirements
The following is required on the server to run Deployment Agent:
- Windows Server 2012 (Windows 8) or newer
- .NET Framework 4.5.2 or newer
- Web Role (IIS) is installed if you are deploying web site
Installing AppVeyor Deployment Agent
- Add new environment with Agent provider selected. Open environment settings and copy Environment access key.
- Download AppVeyor Deployment Agent (.msi)
- Specify Environment access key during Deployment Agent installation.
- Server is ready for deployment.
Unattended Deployment Agent installation
Run the following in PowerShell console:
(new-object net.webclient).DownloadFile('https://www.appveyor.com/downloads/deployment-agent/latest/AppveyorDeploymentAgent.msi', 'AppveyorDeploymentAgent.msi')
msiexec /i AppveyorDeploymentAgent.msi /quiet /qn /norestart /log install.log ENVIRONMENT_ACCESS_KEY=<your_access_key> DEPLOYMENT_GROUP=<your_deployment_group>
Replace <your_access_key> and <your_deployment_group> with your environment access key and your your deployment group respectively.
What artifacts can be deployed
Deployment Agent recognizes artifacts of two types which may contain either web application or Windows application/service:
- Zip archive
- Web Deploy package
To be deployable with Deployment Agent artifact must have a name. Name should not have any spaces. All unnamed artifacts are skipped by Deployment Agent provider.
How to get named artifacts
There are few possible ways of packaging artifact deployable by Agent:
- When Package Web Application projects option is enabled on Build tab of project settings AppVeyor automatically publishes (applies web config transforms) and uploads VS.NET Web Application projects as artifacts named after the name of VS.NET project.
- Specify Deployment name while adding artifact entry on Artifacts tab of project settings.
From script, for example After build script:
appveyor PushArtifact <zip_path> -DeploymentName MyApp
Configuring deployment settings
Use Provider settings of Agent environment to configure which artifacts should be deployed by Agent and how. By default, nothing configured - nothing deployed.
Settings have format <artifact_name>.<setting_name> where <artifact_name> is artifact’s Deployment name.
For example, let the build has the following artifacts:
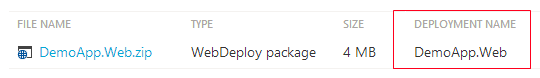
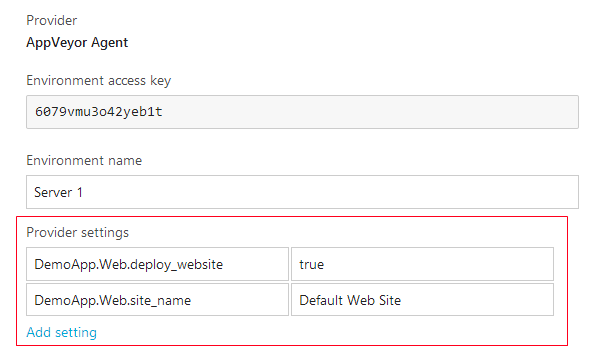
In order for Deployment Agent to deploy that artifact as IIS web site Provider settings will be:
Global settings
There are few settings which have format <setting_name> instead of <artifact_name>.<setting_name>. Those settings are global and apply to each artifact deployment.
agents_expected - Number of remote agents expected to start deployment. Deployment marked as failed if number of agents started deployment is less than expected. Default is 1. Set to 0 to disable this check.
agents_timeout - Time in seconds to wait for remote agents to start deployment. Default is 10 seconds. Minimum is 5 seconds. Maximum is 60 seconds. Increase in case default value of 10 seconds appears to be not enough. Decrease if observe agents always pick up job much faster.
Overriding settings while deploying from build
You can use environment variables for setting values on environment configuration, for example:
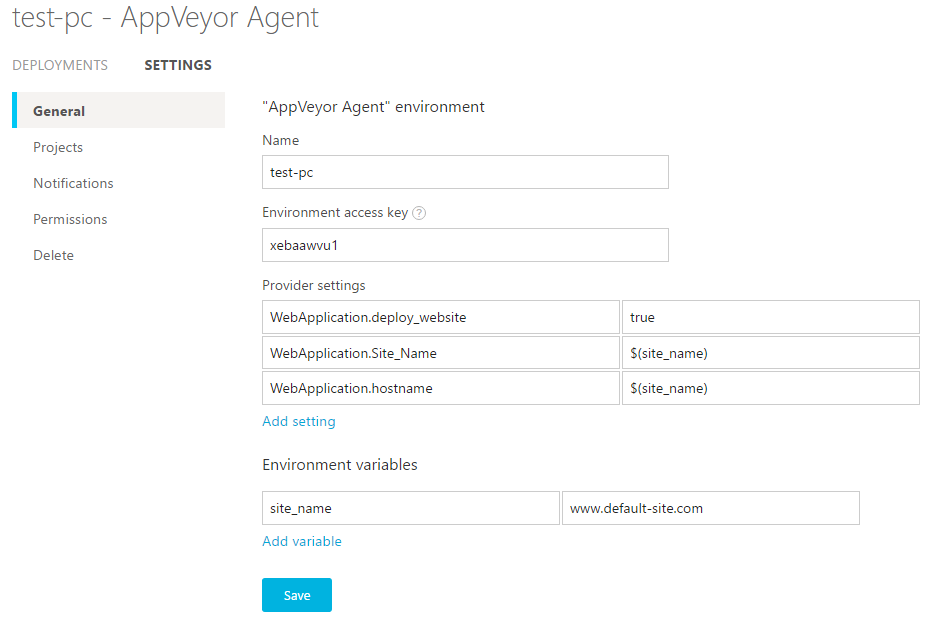
where site_name is environment variable. At the bottom of that screen we are defining its “default” value, i.e. the value used when you deploy from Environments and build environment variables are not present.
However, when you deploy from a build you can override those environment variables like:
deploy:
- provider: Environment
name: test-pc
site_name: www.site-to-deploy.com
Alternatively, that site name can be deployed somewhere during the build, so the following construction is also possible:
environment:
site_to_deploy: www.site-to-deploy.com
deploy:
- provider: Environment
name: test-pc
site_name: $(site_to_deploy)
Deploying artifact package as IIS web site
<artifact_name>.deploy_website: true
Other settings:
site_id- Optional. Site numeric ID.site_name- The name of existing or new website, e.g. “Default Web Site”.application_name- optional web application name (IIS virtual directory) to deploy web app into.application_path- optional root directory for web application (IIS virtual directory).apppool_name- the name of IIS application pool. If pool does not exist it will be created.aspnet_core- Optimize application pool for ASP.NET Core. No needed for classic websites, add and set totruefor ASP.NET Core.port- Port of website binding.ip- IP address of website binding.hostname- Host header value of website binding.protocol- Protocol value of website binding. Could behttp(default if not specified) orhttpsornet.tcp.certificate- Certificate associated withhttpsbinding. This value could be certificate name or thumbprint, for example*.mydomain.comor0B2D18387549968CB4CC30F21D6CC4C0830B679B. If certificate specified protocol is changed tohttps.write_access- When set totrueAgent sets Modify permissions for application pool identity on website root directory.path- Website root directory on the target server. If not specified and website already exists its root directory is not changed.If not specified and website does not exists default directory path is
c:\appveyor\applications\<artifact_name>.remove_files- Agent uses Web Deploy to synchronize website folder contents. By default, it only adds new files and modifies existing.When
remove_filesis set totrueAgent performs full content synchronization, i.e. deletes files at destination that don’t exist in the package.skip_dirs- semicolon list of regular expressions specifying the list of directories to skip while synchronizing web site contents, for example\\App_data;\\uploads.skip_files- semicolon list of regular expressions specifying the list of files to skip while synchronizing web site contents, for exampleweb.config(all web.configs) or only the root config for MVC apps^((?!Views).)*web\.config$(thanks to this blog post).app_offline- places app_offline.htm page into the root of web application before sync to take app offline and then remove the page when deployment has finished.group- Deployment group.deploy_order- Optional. Allows changing the deployment order of artifacts. Artifacts are deployed in ascending order. Deployment order is set to0if not specified.
When deploying web app from Web Deploy package you can use Web Deploy parametrization with environment variables.
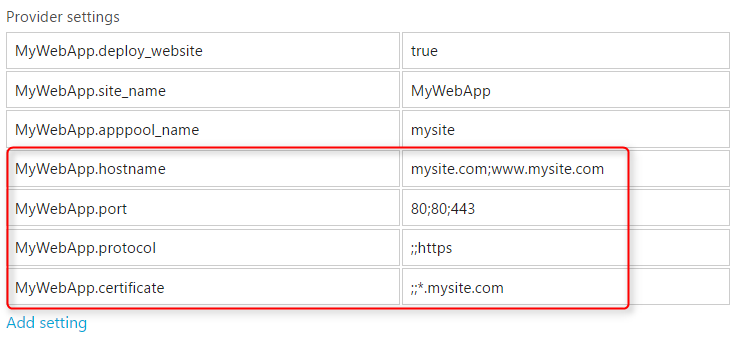
You can specify multiple bindings in hostname, ip and port separated by semi-colon. Below is an example of how 3 bindings can be configured:
- http *:80:mysite.com
- http *:80:www.mysite.com
- https *:443: cert=*.mysite.com
Deploying artifact package as a Windows application
<artifact_name>.deploy_app: true
Other properties:
path- Application root directory. If not specified default application path isc:\appveyor\applications\<artifact_name>.remove_files- Remove additional files at destination.group- Deployment group.skip_dirs- semicolon list of regular expressions specifying the list of directories to skip while synchronizing application folder contents, for example\\Logs;\\files.skip_files- semicolon list of regular expressions specifying the list of files to skip while synchronizing application folder contents.deploy_order- Optional. Allows changing the deployment order of artifacts. Artifacts are deployed in ascending order. Deployment order is set to0if not specified.do_not_start- Optional. Set totrueif Windows Service should not be started after installation.
Deploying artifact package as a Windows service
<artifact_name>.deploy_service: true
Other properties:
service_executable- File name of Windows service executable, e.g.myapp.service.exe. If not specified the first executable found in application directory will be used.service_name- The name of Windows service. If specified Windows service will be created.service_display_name- Display name of Windows service. If not specifiedservice_namewill be used.service_username- The name of user account to run service under. If not specificLocalSystemis used.service_password- User account password ifservice_usernameis set.path- Application root directory. If not specified default application path isc:\appveyor\applications\<artifact_name>.remove_files- Remove additional files at destination.group- Deployment group.skip_dirs- semicolon list of regular expressions specifying the list of directories to skip while synchronizing application folder contents, for example\\Logs;\\files.skip_files- semicolon list of regular expressions specifying the list of files to skip while synchronizing application folder contents.deploy_order- Optional. Allows changing the deployment order of artifacts. Artifacts are deployed in ascending order. Deployment order is set to0if not specified.
Publishing SSDT package artifact to SQL Server
Deployment Agent supports publishing of SSDT package artifacts (with .dacpac extension) to SQL Server instance.
To direct AppVeyor that named artifact should be treated as DACPAC package:
<artifact_name>.deploy_database: true
Other properties:
connection_string- SQL connection string to the target database, for exampleServer=(local)\SQLEXPRESS;Database=my_app;User ID=myuser;Password=password<artifact_name>.<deploy_setting>where<deploy_setting>is a setting described in Publishing SQL Server databases from SSDT packages.<artifact_name>.sqlcmd.<variable_name>- format for specifying SQLCMD variables.
For example, given .dacpac artifact’s deployment name is MyDatabase:
MyDatabase.deploy_database true
MyDatabase.connection_string Server=(local)\SQLEXPRESS;Database=my_app;Integrated security=SSPI;
MyDatabase.sqlcmd.MYVAR hello, world!
MyDatabase.backup_database_before_changes true
deploy_order- Optional. Allows changing the deployment order of artifacts. Artifacts are deployed in ascending order. Deployment order is set to0if not specified.
Installing MSI package artifact on remote machine
With AppVeyor Deployment Agent you can run the installation of MSI artifact (with .msi extension) on the remote machine. Agent uses msiexec command-line utility to install the package. MSI package should support silent mode (/quiet switch). We recommend using WiX for building application installation packages.
<artifact_name>.deploy_msi: true
Other properties:
uninstall_application- if this setting is set the agent will try to uninstall the previous version of the application before installing a new one. Application name should be the same as you see in “Add/Remove Programs” control panel snap-in.<artifact_name>.<property_name>- set<property_name>MSI custom property while installing the app. All properties are addedt tomsiexeccommand asPROPERTY="VALUE" PROPERTY="VALUE" ....
For example, given .msi artifact’s deployment name is MyAppInstall:
MyAppInstall.deploy_msi true
MyAppInstall.uninstall_application My Application
Running PowerShell scripts on target server during deployment
before-deploy.ps1 PowerShell script in the root of application folder will be called before every deployment. deploy.ps1 PowerShell script in the root of application folder will be called after every successful deployment.
During scripts execution the following environment variables are available:
Job details:
APPVEYOR- script runs in AppVeyor environmentCI- script runs in AppVeyor environmentAPPVEYOR_PROJECT_ID- Unique system ID of projectAPPVEYOR_PROJECT_NAME- Project display nameAPPVEYOR_PROJECT_SLUG- Project slug that you can see in URL, e.g. myproject-123APPVEYOR_BUILD_ID- Unique system ID of buildAPPVEYOR_BUILD_NUMBER- Build number of deploying artifactAPPVEYOR_BUILD_VERSION- Build version on deploying artifactAPPVEYOR_JOB_ID- Unique system ID of deployment jobAPPVEYOR_REPO_NAME- Repository name in the formowner-name/repo-nameAPPVEYOR_REPO_BRANCH- Build branchAPPVEYOR_REPO_TAG-trueif build has started by pushed tag; otherwisefalse.APPVEYOR_REPO_TAG_NAME- contains tag name for builds started by tag; otherwise this variable is undefined.APPVEYOR_REPO_COMMIT- Build commit ID (SHA)APPVEYOR_REPO_COMMIT_AUTHOR- Commit authorAPPVEYOR_REPO_COMMIT_AUTHOR_EMAIL- Commit author’s emailAPPVEYOR_REPO_COMMIT_TIMESTAMP- Commit timestampAPPVEYOR_REPO_COMMIT_MESSAGE- Commit message
Application details:
APPLICATION_NAME- application name (artifact deployment name)APPLICATION_DEPLOY_WEBSITE-trueif artifact deployed as IIS web siteAPPLICATION_PATH- application or website root folderAPPLICATION_REMOVE_FILES- perform full sync of package/application folder contents, i.e. remove additional files at destinationAPPLICATION_SITE_NAME- IIS web site name
Artifact details:
ARTIFACT_FILENAME- artifact file name as in cloud storageARTIFACT_LOCALPATH- local file name of downloaded artfact packageARTIFACT_NAME- artifact deployment nameARTIFACT_SIZE- package size in bytesARTIFACT_TYPE- artifact typeARTIFACT_URL- artifact package download URL valid for 10 minutes
Calling script block once per deployment
In your before-deploy.ps1 or deploy.ps1 use the following code to run once per deployment/per cluster:
if (Enter-OncePerDeployment "block_name")
{
# your code that must be run once per cluster
}
Replace block_name with some value identifying operations inside the block, e.g. “install_sql”
Troubleshooting
Open Event Viewer, expand Applications and Services Logs node and navigate to Deployment Agent event log.